研究成果
Oct, 2023
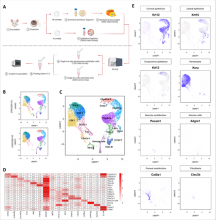
Purpose: To generate a single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) map and construct cell-cell communication networks of mouse corneas.
Methods: C57BL/6 mouse corneas were dissociated to single cells and subjected to scRNA-seq. Cell populations were clustered and annotated for bioinformatic analysis using the R package ""Seurat."" Differential expression patterns were validated and spatially mapped with whole-mount immunofluorescence staining. Global intercellular signaling networks were constructed using CellChat.
Results: Unbiased clustering of scRNA-seq transcriptomes of 14,732 cells from 40 corneas revealed 17 cell clusters of six major cell types: nine epithelial cell, three keratocyte, two corneal endothelial cell, and one each of immune cell, vascular endothelial...

Oct, 2023
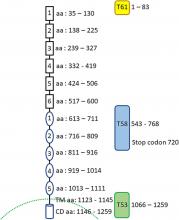
Neuroblastoma, a childhood cancer affecting the sympathetic nervous system, continues to challenge the development of potent treatments due to the limited availability of druggable targets for this aggressive illness. Recent investigations have uncovered that phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase (PHGDH), an essential enzyme for de novo serine synthesis, serves as a non-oncogene dependency in high-risk neuroblastoma. In this study, we show that homoharringtonine (HHT) acts as a PHGDH inhibitor, inducing intricate alterations in cellular metabolism, and thus providing an efficient treatment for neuroblastoma. We have experimentally verified the reliance of neuroblastoma on PHGDH and employed molecular docking, thermodynamic evaluations, and X-ray crystallography techniques to determine the bond...
Sep, 2023
Hirschsprung disease (HSCR) is a congenital disorder of functional bowel obstruction due to the absence of enteric ganglia in distal bowel. Different L1cam variants were reportedly associated with L1cam syndrome and HSCR, whose phenotypes lacked predictable relevance to their genotypes. Using next-generation sequencing (NGS), we found an L1CAM de novo frameshift mutation in a female with mild hydrocephalus and skip-type HSCR. A nearly identical L1cam variant was introduced into FVB/NJ mice via the CRISPR-EZ method. A silent mutation was created via ssODN to gain an artificial Ncol restriction enzyme site for easier genotyping. Six L1cam protein-coding alternative transcripts were quantitatively measured. Immunofluorescence staining with polyclonal and monoclonal L1cam antibodies was used...

Sep, 2023
Antrodia cinnamomea is an endemic species found in Taiwan, known for its medicinal properties in treating various discomforts, including inflammation, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and other diseases. A. cinnamomea contains terpenoids that exhibit numerous bioactivities, making them potential food additives. This discovery piqued our interest in uncovering their biosynthetic pathway. Herein, we conducted functional and structural characterization of a sesquiterpene synthase Cop4 from A. cinnamomea (AcCop4). Through gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis, we observed that AcCop4 catalyzes the cyclization of farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP), primarily producing cubebol. Cubebol is widely used as a long-lasting cooling and refreshing agent in the food industry. The structure of AcCop4,...
Sep, 2023
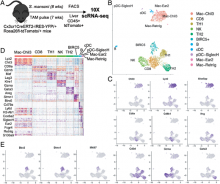
Our previous studies identified a population of stem cell-like proliferating myeloid cells within inflamed tissues that could serve as a reservoir for tissue macrophages to adopt different activation states depending on the microenvironment. By lineage-tracing cells derived from CX3CR1+ precursors in mice during infection and profiling by single-cell RNA sequencing, in this study, we identify a cluster of BIRC5+ myeloid cells that expanded in the liver during chronic infection with either the parasite Schistosoma mansoni or the bacterial pathogen Staphylococcus aureus. In the absence of tissue-damaging toxins, S. aureus infection does not elicit these BIRC5+ cells. Moreover, deletion of BIRC5 from CX3CR1-expressing cells results in improved survival during S. aureus infection. Hence the...
Sep, 2023
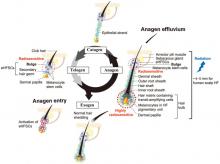
Because hair follicles (HFs) are highly sensitive to ionizing radiation, radiotherapy-induced alopecia (RIA) is a core adverse effect of oncological radiotherapy. Yet, effective RIA-preventive therapy is unavailable because the underlying pathobiology remains underinvestigated. Aiming to revitalize interest in pathomechanism-tailored RIA management, we describe the clinical RIA spectrum (transient, persistent, progressive alopecia) and our current understanding of RIA pathobiology as an excellent model for studying principles of human organ and stem cell repair, regeneration, and loss. We explain that HFs respond to radiotherapy through two distinct pathways (dystrophic anagen or catagen) and why this makes RIA management so challenging. We discuss the responses of different HF cell...
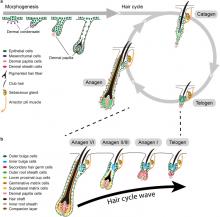
Sep, 2023
Researchers should be aware that hair growth cycle drives prominent molecular, cellular, and morphological changes to the entire skin. Thus, hair growth constitutes a major experimental variable that influences the interpretation of dermatological studies. Hair growth in mice is neither asynchronous nor fully synchronized; rather, it occurs in waves that dynamically propagate across the skin. In consequence, any given area of mouse skin can contain hair follicles in different stages of the cycle in close physical proximity. Furthermore, hair growth waves in mice are initiated by probabilistic events at different time points and across stochastic locations. The consequence of such stochasticity is that precise patterns of hair growth waves differ from mouse to mouse, even in littermates of...
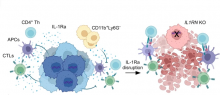
Aug, 2023
Background: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) is a pernicious disease characterized by an immunosuppressive milieu that is unresponsive to current immunotherapies. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) is a natural anti-inflammatory cytokine; however, its contribution to cancer pathogenesis and immunosuppression remains elusive. In this research, we investigated the role and mechanism of IL-1Ra in malignant progression of PDA.
Results: Through analyzing clinical dataset and examining the pathological tumor tissues and serum samples, we have demonstrated that IL-1Ra expression is elevated in human PDA and positively associated with malignant progression of PDA. To study the biological function of IL-1Ra in tumors, we generated a set of mouse pancreatic cancer cell lines with a...
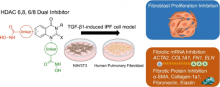
Aug, 2023
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is incurable, and its progression is difficult to control and thus can lead to pulmonary deterioration. Pan-histone deacetylase inhibitors such as SAHA have shown potential for modulating pulmonary fibrosis yet with off-target effects. Therefore, selective HDAC inhibitors would be beneficial for reducing side effects. Toward this goal, we designed and synthesized 24 novel HDAC6, HDAC8, or dual HDAC6/8 inhibitors and established a two-stage screening platform to rapidly screen for HDAC inhibitors that effectively mitigate TGF-β-induced pulmonary fibrosis. The first stage consisted of a mouse NIH-3T3 fibroblast prescreen and yielded five hits. In the second stage, human pulmonary fibroblasts (HPFs) were used, and four out of the five hits were tested for caco-2...

Aug, 2023
Introduction: Cisplatin, a commonly used anticancer compound, exhibits severe off-target organ toxicity. Due to its wide application in cancer treatment, the reduction of its damage to normal tissue is an imminent clinical need. Cisplatin-induced testicular oxidative stress and damage lead to male sub- or infertility. Despite earlier studies showing that the natural polyphenol extracts honokiol serve as the free radical scavenger that reduces the accumulation of intracellular free radicals, whether honokiol exhibits direct effects on the testis and sperm is unclear. Thus, the aim of the current study is to investigate the direct effects of honokiol on testicular recovery and sperm physiology.
Methods: We encapsulated this polyphenol antioxidation compound into liposome-based...