研究成果

Dec, 2025
Background
Tumor-specific CD8+ T lymphocytes play a critical role in anticancer immunity but frequently become dysfunctional and exhausted within the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Although immune checkpoint inhibitors can restore T-cell activity, resistance to these treatments remains a significant challenge. Therefore, understanding the transcriptional and regulatory mechanisms underlying CD8+ T-cell exhaustion is crucial for the development of effective therapies.
Methods
We developed two murine models of acquired immune checkpoint inhibitor resistance through prolonged anti-PD1 treatment. To gain insight into CD8+ T-cell exhaustion, we performed single-cell multiomics analysis, including both scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq, to capture gene expression profiles and chromatin...

Oct, 2025
Secondary growth is a key characteristic evolved from seed plants and generates secondary xylem-the most abundant tissue on Earth. Recent studies have uncovered xylem developmental lineages in eudicots and magnoliids of angiosperms. However, xylem development in gymnosperms, the other representative clade of seed plants, remained elusive. We performed single-cell transcriptomics for xylem cells of conifers (Cunninghamia lanceolata), the major clade in gymnosperms. Using Seurat and scVI-based cross-species integration, we reconstructed the xylem differentiation trajectories and revealed that the radial system is conserved across seed plants, while the axial system in C. lanceolata exhibits a composite lineage architecture resembling both eudicots and magnoliids. To validate these...

Oct, 2025
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a fundamental mechanism involved in the morphogenesis of metazoans. Through this evolutionarily conserved multi-stage process, cells acquire quasi-epithelial to multiple intermediate morphologies with epithelial and mesenchymal attributes, rarely reaching a complete mesenchymal phenotype. Complex evolutionary-conserved morphogenetic movements in gastrulation are described extensively, as they exemplify the extent of epithelial cell plasticity in the animal kingdom. Nonetheless, a single-gene knockout can modify the mode of gastrulation while achieving the same body plan. Numerous interconnected mechanisms drive different degrees of EMT, including surface receptor signaling, metabolism, and epigenetics. EMT is reactivated in adult tissues during...

Aug, 2025
Background and aims: Germline genetic factors influence the clinical features of colorectal cancer (CRC); however, these factors remain underexplored in Taiwan. This study aims to evaluate the pathogenicity of germline variants and investigate their associations with familial risk and early-onset CRC. Methods: Whole-exome sequencing of 600 Taiwanese CRC patients was analyzed, assessing variant pathogenicity using American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) guidelines. Comparative analysis with 1,492 controls identified candidate genes, and clinical features were correlated with genetic variants. Results: We identified several novel candidate genes, including CCDC18 and CEP135. A total of 24 pathogenic variants in hereditary cancer genes were found in 5.2% of Taiwanese CRC...

Jul, 2025
Neuroblastoma is the most common heterogeneous solid tumor in children, and current treatment options remain limited, especially for high-risk patients. Previous studies have identified dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH), a key enzyme in pyrimidine synthesis, as a potential therapeutic target in cancer. However, none of the existing FDA-approved DHODH inhibitors have shown effective inhibition of neuroblastoma cell growth. To address this challenge, we employed virtual screening to discover potential DHODH-targeting drugs, identifying Regorafenib as a promising candidate. Regorafenib significantly inhibited neuroblastoma growth in both neuroblastoma cells and patient-derived organoids. To unravel the underlying molecular mechanisms, we conducted Tandem Mass Tag (TMT)-based quantitative...
Jul, 2025
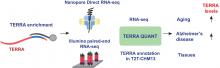
Telomeric repeat-containing RNA (TERRA), transcribed from subtelomeric regions toward telomeric ends, poses challenges in deciphering its complete sequences. Utilizing TERRA-capture RNA-seq and Oxford Nanopore direct RNA sequencing to acquire full-length TERRA, we annotate TERRA transcription regions in the human T2T-CHM13 reference genome. TERRA transcripts encompass hundreds to over a thousand nucleotides of telomeric repeats, predominantly originating from 61-29-37 bp repeat promoters enriched with H3K4me3, RNA Pol II, CTCF, and R-loops. We develop a bioinformatics tool, TERRA-QUANT, for quantifying TERRA using RNA-seq datasets and find that TERRA increases with age in blood, brain, and fibroblasts. TERRA upregulation in aged leukocytes is confirmed by reverse transcription...

Jul, 2025
Neuroblastoma, a prevalent and aggressive childhood cancer, lacks effective treatments. Recent research highlights the repurposing of existing drugs as a strategy for breakthroughs in combating this disease. We systematically analyzed small-molecule perturbation gene expression data from the Library of Integrated Network-Based Cellular Signatures (LINCS), identifying pyrvinium pamoate and sirolimus, two FDA-approved drugs, as potential candidates for neuroblastoma combination therapy. Colony formation assays and organoid culture confirmed that the therapeutic effect of combining these two drugs exceeded that of either drug alone. The mRNA expression levels of several genes predicted by LINCS also decreased. To comprehensively understand the mechanism behind superior efficacy of the...

Jul, 2025
Doxorubicin (DOX), although effective in treating cancer, has significant cardiac side effects, which limit its clinical utility. In this study, we collected time-course transcriptomics and metabolomics data from the human cardiomyocyte cell line AC16, which we analyzed along with curated public transcriptomics data on DOX-induced toxicity. We developed a multiomics analysis workflow and a computational toolbox, pipeGEM, to integrate RNA-seq data with metabolic models, enabling the simulation of DOX-induced metabolic perturbations at a sample-specific level. Our results revealed that DOX affected mitochondrial damage and mitochondria-to-nucleus retrograde signaling, potentially contributing to the observed cellular enlargement, senescence and metabolic shift. Cardiac cells that survived...

Jun, 2025
Background: High-throughput sequencing has revolutionized genetic disorder diagnosis, but variant pathogenicity interpretation is still challenging. Even though the human genome variation society (HGVS) provides recommendations for variant nomenclature, discrepancies in annotation remain a significant hurdle. Results: In this study, we evaluated the annotation concordance between three tools-ANNOVAR, SnpEff, and variant effect predictor (VEP)-using 164,549 two-star variants from ClinVar. The analysis used HGVS nomenclature string-match comparisons to assess annotation consistency from each tool, corresponding coding impacts, and associated ACMG criteria inferred from the annotations. The analysis revealed variable concordance rates, with 58.52% agreement for HGVSc, 84.04% for HGVSp, and...

Jun, 2025
Evaluating robustness of somatic mutation detections is essential when using whole-exome sequencing (WES) for treatment decision-making. A comprehensive evaluation was conducted using tumor WES from the US Food and Drug Administration-led Sequencing Quality Control Phase 2 project, in which multiple library kits sequenced identical DNA materials across three laboratories to benchmark analytical validity. These workflows included various read aligner (BWA, Bowtie2, DRAGEN-Aligner, DRAGMAP, and HISAT2) and mutation caller (Mutect2, TNscope, DRAGEN-Caller, and DeepVariant) combinations. The results revealed that DRAGEN exhibited superior performance, achieving mean F1 scores of 0.966 and 0.791 for single-nucleotide variant and insertion/deletion detection, respectively. Among open-source...