研究成果

Sep, 2023
Antrodia cinnamomea is an endemic species found in Taiwan, known for its medicinal properties in treating various discomforts, including inflammation, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and other diseases. A. cinnamomea contains terpenoids that exhibit numerous bioactivities, making them potential food additives. This discovery piqued our interest in uncovering their biosynthetic pathway. Herein, we conducted functional and structural characterization of a sesquiterpene synthase Cop4 from A. cinnamomea (AcCop4). Through gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis, we observed that AcCop4 catalyzes the cyclization of farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP), primarily producing cubebol. Cubebol is widely used as a long-lasting cooling and refreshing agent in the food industry. The structure of AcCop4,...
Sep, 2023
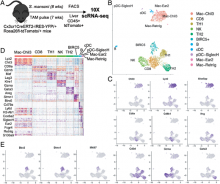
Our previous studies identified a population of stem cell-like proliferating myeloid cells within inflamed tissues that could serve as a reservoir for tissue macrophages to adopt different activation states depending on the microenvironment. By lineage-tracing cells derived from CX3CR1+ precursors in mice during infection and profiling by single-cell RNA sequencing, in this study, we identify a cluster of BIRC5+ myeloid cells that expanded in the liver during chronic infection with either the parasite Schistosoma mansoni or the bacterial pathogen Staphylococcus aureus. In the absence of tissue-damaging toxins, S. aureus infection does not elicit these BIRC5+ cells. Moreover, deletion of BIRC5 from CX3CR1-expressing cells results in improved survival during S. aureus infection. Hence the...
Sep, 2023
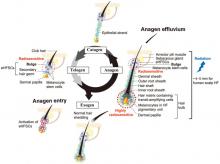
Because hair follicles (HFs) are highly sensitive to ionizing radiation, radiotherapy-induced alopecia (RIA) is a core adverse effect of oncological radiotherapy. Yet, effective RIA-preventive therapy is unavailable because the underlying pathobiology remains underinvestigated. Aiming to revitalize interest in pathomechanism-tailored RIA management, we describe the clinical RIA spectrum (transient, persistent, progressive alopecia) and our current understanding of RIA pathobiology as an excellent model for studying principles of human organ and stem cell repair, regeneration, and loss. We explain that HFs respond to radiotherapy through two distinct pathways (dystrophic anagen or catagen) and why this makes RIA management so challenging. We discuss the responses of different HF cell...
Sep, 2023
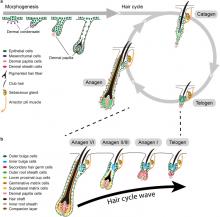
Researchers should be aware that hair growth cycle drives prominent molecular, cellular, and morphological changes to the entire skin. Thus, hair growth constitutes a major experimental variable that influences the interpretation of dermatological studies. Hair growth in mice is neither asynchronous nor fully synchronized; rather, it occurs in waves that dynamically propagate across the skin. In consequence, any given area of mouse skin can contain hair follicles in different stages of the cycle in close physical proximity. Furthermore, hair growth waves in mice are initiated by probabilistic events at different time points and across stochastic locations. The consequence of such stochasticity is that precise patterns of hair growth waves differ from mouse to mouse, even in littermates of...
Aug, 2023
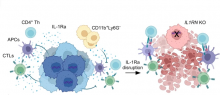
Background: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) is a pernicious disease characterized by an immunosuppressive milieu that is unresponsive to current immunotherapies. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) is a natural anti-inflammatory cytokine; however, its contribution to cancer pathogenesis and immunosuppression remains elusive. In this research, we investigated the role and mechanism of IL-1Ra in malignant progression of PDA.
Results: Through analyzing clinical dataset and examining the pathological tumor tissues and serum samples, we have demonstrated that IL-1Ra expression is elevated in human PDA and positively associated with malignant progression of PDA. To study the biological function of IL-1Ra in tumors, we generated a set of mouse pancreatic cancer cell lines with a...
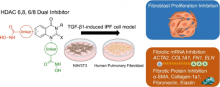
Aug, 2023
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is incurable, and its progression is difficult to control and thus can lead to pulmonary deterioration. Pan-histone deacetylase inhibitors such as SAHA have shown potential for modulating pulmonary fibrosis yet with off-target effects. Therefore, selective HDAC inhibitors would be beneficial for reducing side effects. Toward this goal, we designed and synthesized 24 novel HDAC6, HDAC8, or dual HDAC6/8 inhibitors and established a two-stage screening platform to rapidly screen for HDAC inhibitors that effectively mitigate TGF-β-induced pulmonary fibrosis. The first stage consisted of a mouse NIH-3T3 fibroblast prescreen and yielded five hits. In the second stage, human pulmonary fibroblasts (HPFs) were used, and four out of the five hits were tested for caco-2...

Aug, 2023
Introduction: Cisplatin, a commonly used anticancer compound, exhibits severe off-target organ toxicity. Due to its wide application in cancer treatment, the reduction of its damage to normal tissue is an imminent clinical need. Cisplatin-induced testicular oxidative stress and damage lead to male sub- or infertility. Despite earlier studies showing that the natural polyphenol extracts honokiol serve as the free radical scavenger that reduces the accumulation of intracellular free radicals, whether honokiol exhibits direct effects on the testis and sperm is unclear. Thus, the aim of the current study is to investigate the direct effects of honokiol on testicular recovery and sperm physiology.
Methods: We encapsulated this polyphenol antioxidation compound into liposome-based...
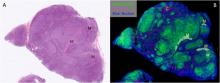
Aug, 2023
Background: Reactive lymphadenopathies such as toxoplasmosis and cytomegalovirus lymphadenitis are associated with monocytoid cell proliferation. Monocytoid cells are B-lymphocytes with an undetermined subset.
Methods: Using digital spatial profiling whole transcriptome analyses, this study compared monocytoid and control B-cells. The B-cell subset of monocytoid cells was assigned according to gene expression profiles.
Results: This study identified 466 differentially expressed genes between monocytoid and control B-cells. The cellular deconvolution algorithm identified monocytoid cells as memory B-cells instead of as naïve B-cells. A comparison of the upregulated genes revealed that atypical memory B-cells had the largest number of genes overlapping with monocytoid cells compared with...
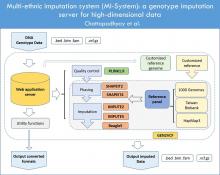
Jul, 2023
Objective: Genotype imputation is a commonly used technique that infers un-typed variants into a study's genotype data, allowing better identification of causal variants in disease studies. However, due to overrepresentation of Caucasian studies, there's a lack of understanding of genetic basis of health-outcomes in other ethnic populations. Therefore, facilitating imputation of missing key-predictor-variants that can potentially improve a risk health-outcome prediction model, specifically for Asian ancestry, is of utmost relevance.
Methods: We aimed to construct an imputation and analysis web-platform, that primarily facilitates, but is not limited to genotype imputation on East-Asians. The goal is to provide a collaborative imputation platform for researchers in the public...
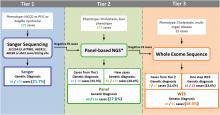
Jul, 2023
Objectives: To determine how advanced genetic analysis methods may help in clinical diagnosis.
Study design: We report a combined genetic diagnosis approach for patients with clinical suspicion of genetic liver diseases in a tertiary referral center, using tools either tier 1: Sanger sequencing on SLC2SA13, ATP8B1, ABCB11, ABCB4, and JAG1 genes, tier 2: panel-based next generation sequencing (NGS), or tier 3: whole-exome sequencing (WES) analysis.
Results: In a total of 374 patients undergoing genetic analysis, 175 patients received tier 1 Sanger sequencing based on phenotypic suspicion, and pathogenic variants were identified in 38 patients (21.7%). Tier 2 included 216 patients (39 of tier 1-negative patients) who received panel-based NGS, and pathogenic variants were identified in 60...